David G.T. Barrett--DeepMind
我们通过离散步骤的梯度下降损失轨迹来构造网络正则化模型,称之为隐式正则化模型,并通过反向误差算法计算正则化项。理论和实验表明,该正则化模型会使网络的解趋向于平坦极小值,且网络的鲁棒性更好。
1. 引言
问题背景:深度神经网络损失函数的曲面多是高度非凸的,梯度下降算法通常能手沿着最陡峭的下降方向朝着最小值的子流形变化。然而,离散化算法所带来的误差积累到一定程度会严重影响网络的性能。为了解决这一问题,我们首先使用反向误差分析计算修改后的损失和原始损失之间的差异,并发现它与损失梯度的二阶矩成正比,我们称之为隐式梯度正则化(IGR)。通过微分几何方法,我们发现IGR与损失表面斜率的平方成正比,损失越小优化算法,网络越趋近于平坦极小值。我们还发现 IGR 可以解释学习率大小与测试准确性和模型稳健性相关的观察结果。 最后,证明了 IGR 可以用作显式正则化器,使其超出最大可能的隐式梯度正则化强度
关键词: Gradient Regularization, backward error, flatter optima, Runge-Kutta methods.
目标会议/期刊,ICLR 2021
文章主要结论
Theorem 3.1. Let E be a sufficiently differentiable function on a parameter space ��∈��^��. The modified equation for gradient flow �� ̇=−��_�� ��(��) is of the form

Where 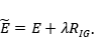
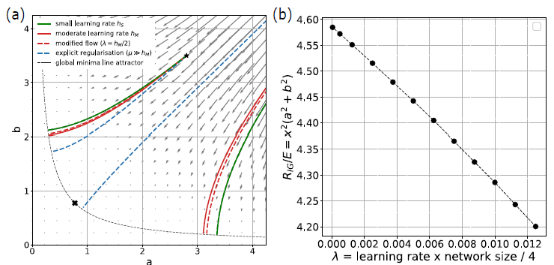
Definition: Implicit gradient regularization(IGR) is the implicit regularization behavior originating from the use of discrete update steps in gradient descent, as characterized by Equation.
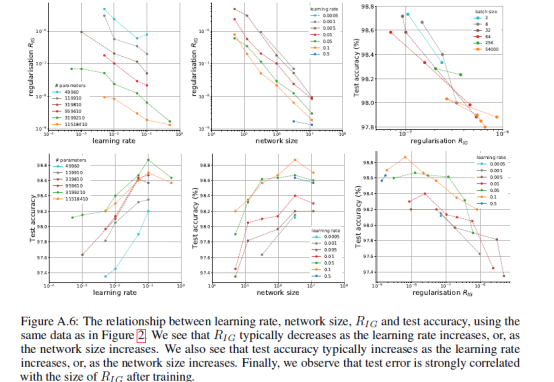
Prediction 2.1: IGR encourages smaller values of RIG(θ) relative to the loss E(θ).
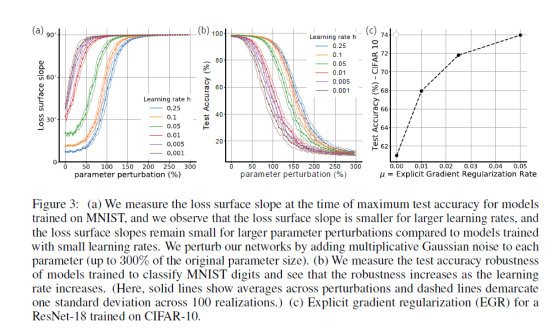
Prediction 2.2: IGR encourages the discovery of flatter optima.
Prediction 2.3: IGR encourages higher test accuracy.
Prediction 2.4: IGR encourages the discovery of optima that are more robust to parameter perturbations.

2. 领域代表性工作
[1] Vaishnavh Nagarajan and J Zico Kolter. Gradient descent gan optimization is locally stable. In Advances in neural information processing systems, volume 30. 2017.
[2] David Balduzzi, Sebastien Racaniere, James Martens, Jakob Foerster, Karl Tuyls, and Thore Graepel.The mechanics of n-player differentiable games. In International Conference on Machine Learning,volume 80, 2018.
[3] Lars Mescheder, Sebastian Nowozin, and Andreas Geiger. The numerics of gans. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, volume 30. 2017.
[4] Chongli Qin, Yan Wu, Jost Tobias Springenberg, Andrew Brock, Jeff Donahue, Timothy P. Lillicrap, and Pushmeet Kohli. Training generative adversarial networks by solving ordinary differential equations. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, volume 33. 2020.
3. 研究团队这作者介绍
DeepMind一家英国的人工智能公司,由人工智能程序师兼神经科学家Demis Hassabis等人于2010年联合创立,最初名称是DeepMind科技(DeepMind Technologies Limited),在2014年被谷歌收购。 公司将机器学习和系统神经科学的最先进技术结合起来,建立强大的通用学习算法,最初成果主要应用于模拟、电子商务、游戏开发等商业领域,之后将逐步应用到医疗保健等领域。
参考文献
1) Alnur Ali, J. Zico Kolter, and Ryan J. Tibshirani. A continuous-time view of early stopping for least squares regression. In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, volume 89, 2019.
2) Sanjeev Arora, Simon Du, Wei Hu, Zhiyuan Li, and Ruosong Wang. Fine-grained analysis of optimization and generalization for overparameterized two-layer neural networks. In International Conference on Machine Learning, volume 97, 2019b.
3) Mikhail Belkin, Daniel Hsu, Siyuan Ma, and Soumik Mandal. Reconciling modern machine-learning practice and the classical bias–variance trade-off. In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, volume 116, 2019.
4) Yuanyuan Feng, Tingran Gao, Lei Li, Jian-guo Liu, and Yulong Lu. Uniform-in-time weak error analysis for stochastic gradient descent algorithms via diffusion approximation. Communications in Mathematical Sciences, 18, 2020.
5) Moritz Hardt, Ben Recht, and Yoram Singer. Train faster, generalize better: Stability of stochastic gradient descent. In International Conference on Machine Learning, volume 48, 2016.