近日,实验室博士生赵颖闻关于蛋白质功能预测的研究成果被期刊IEEE Journal of Biomedical Health Informatics(JBHI)录用。JBHI属于JCR一区、CCF推荐C类期刊,影响因子为7.7。
题目:Predicting Protein Functions Based on Heterogeneous Graph Attention Technique
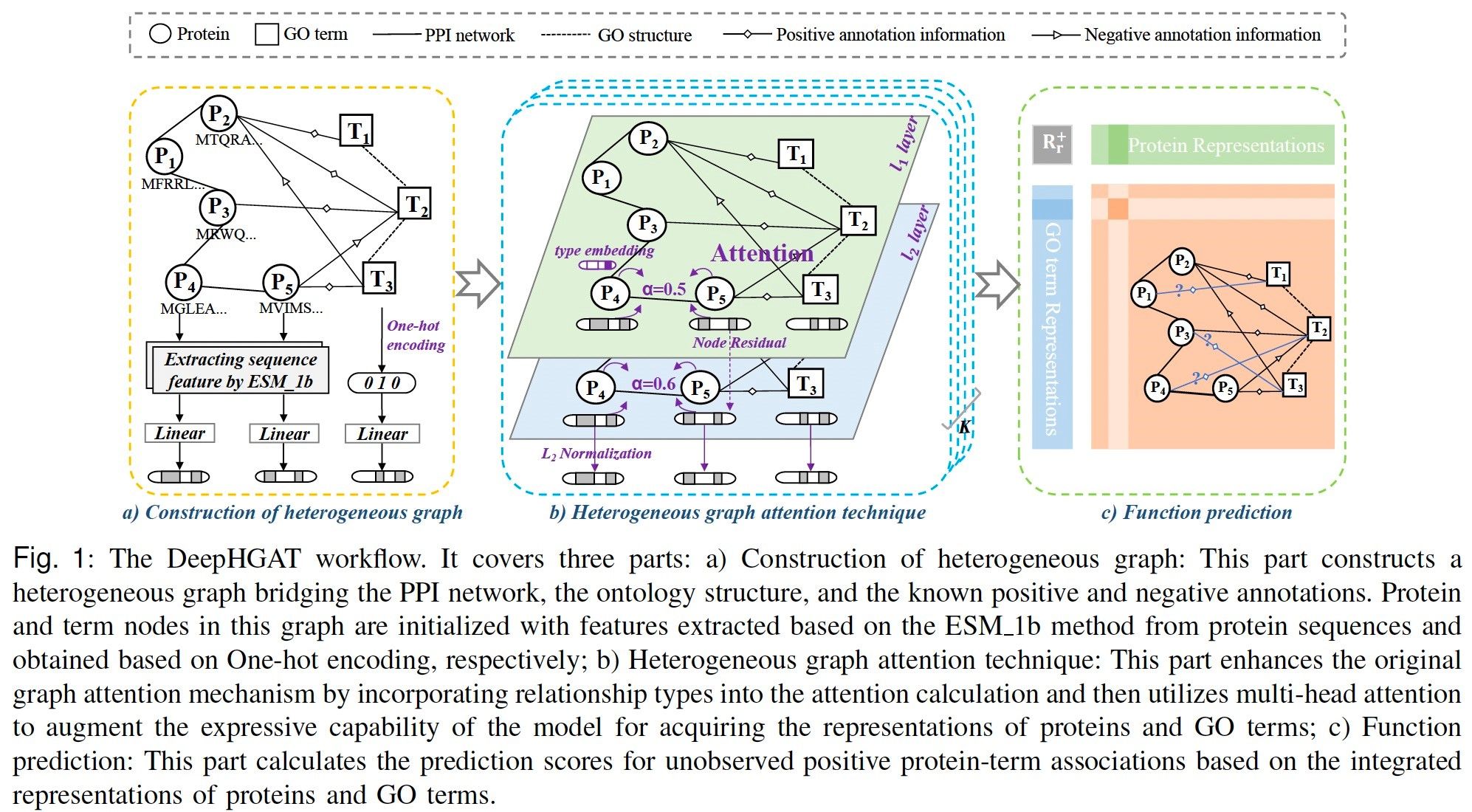
摘要:In bioinformatics, protein function prediction stands as a fundamental area of research and plays a crucial role in addressing various biological challenges, such as the identification of potential targets for drug discovery and the elucidation of disease mechanisms. However, known functional annotation databases usually provide positive experimental annotations that proteins carry out a given function, and rarely record negative experimental annotations that proteins do not carry out a given function. Therefore, existing computational methods based on deep learning models focus on these positive annotations for prediction and ignore these scarce but informative negative annotations, leading to an underestimation of precision. To address this issue, we introduce a deep learning method that utilizes a heterogeneous graph attention technique. The method first constructs a heterogeneous graph that covers the protein-protein interaction network, ontology structure, and positive and negative annotation information. Then, it learns embedding representations of proteins and ontology terms by using the heterogeneous graph attention technique. Finally, it leverages these learned representations to reconstruct the positive protein-term associations and score unobserved functional annotations. It can enhance the predictive performance by incorporating these known limited negative annotations into the constructed heterogeneous graph. Experimental results on three species (i.e., Human, Mouse, and Arabidopsis) demonstrate that our method can achieve better performance in predicting new protein annotations than state-of the-art methods.
简介:在生物信息学领域,蛋白质功能预测是一个基础性的研究任务,对于识别潜在的药物靶点和揭示疾病机理等方面具有关键作用。然而,已知的功能注释数据库通常仅提供蛋白质执行特定功能的正标注,很少记录蛋白质不执行特定功能的负标注。因此,现有的基于深度学习模型的计算方法侧重于利用这些正标注进行预测,而忽略了这些虽然稀缺但信息丰富的负标注,从而导致了精确度被低估的问题。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一种基于异构图注意力技术的深度学习方法。该方法首先构建了一个涵盖蛋白质相互作用网络、本体结构以及正负标注信息的异构图。然后,利用异构图注意力技术学习蛋白质和本体术语的嵌入表示。最后,利用这些学习到的表示来重建蛋白质-术语关联,并对未观察到的功能注释进行评分。通过将这些已知但有限的负标注纳入构建的异构图中,可以提高预测性能。三个物种(人类、小鼠和拟南芥)的实验结果表明,我们的方法在预测新的蛋白质注释方面比最先进的方法表现更好。